Nepal’s Economic Overview: Mid-February 2024
KATHMANDU: The Economic Research Department of Nepal Rastra Bank presents a comprehensive snapshot of Nepal’s macroeconomic and financial landscape, based on seven months of data ending in mid-February of the fiscal year 2023/24. Here are the key highlights:
Inflation Trends:
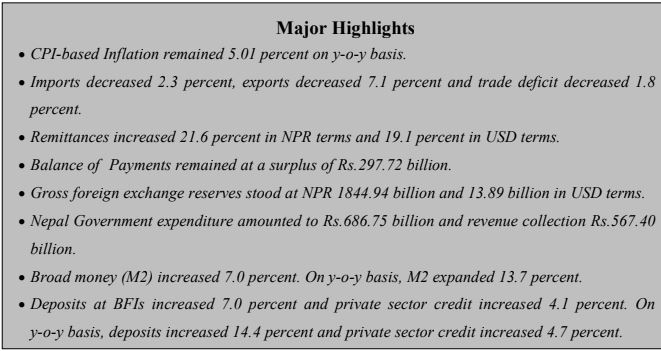
Year-on-year consumer price inflation moderated to 5.01% in mid-February 2024, down from 7.88% a year ago.
Food and beverage category inflation stood at 6.51%, while the non-food and service category inflation was 3.85%.
Price Indices:
In the Food and Beverage Category, notable increases were observed in the price index of spices (32.11%) and pulses & legumes (11.15%).
Under the Non-Food and Services Category, sectors like recreation & culture (12.61%) and miscellaneous goods & services (9.15%) experienced upward price trends.
Regional Inflation Variation:
The year-on-year consumer price inflation varied across regions, with the Kathmandu Valley at 4.96%, Terai at 4.71%, Hill at 5.58%, and Mountain at 5.44%.
Wholesale Price Dynamics:
Year-on-year wholesale price inflation was at 2.82% in mid-February 2024, a significant decrease from 9.67% a year ago.
Notable changes in the wholesale price index were observed in consumption goods (7.05%) and capital goods (1.79%).
Trade Performance:
Merchandise exports decreased by 7.1% to Rs. 86.83 billion, with significant fluctuations in exports to India, other countries, and an impressive surge in exports to China (338.8%).
Merchandise imports saw a 2.3% decrease, totaling Rs. 897.94 billion, marked by variations in imports from India, other countries, and a substantial increase from China (38.4%).
Balance of Payments and Exchange Rates:
The Balance of Payments registered a surplus of Rs. 297.72 billion, reflecting stability and positive economic performance.
Gross foreign exchange reserves increased by 19.9% to Rs. 1844.94 billion, with the Nepalese currency depreciating by 1.05% against the US dollar.
Government Finances:
Total government expenditure stood at Rs. 686.75 billion, showcasing a 2.9% increase, with recurrent, capital, and financial expenditures at Rs. 509.04 billion, Rs. 63.58 billion, and Rs. 114.13 billion, respectively.
Total revenue mobilization of the Nepal Government reached Rs. 567.40 billion, displaying a growth of 10.2%.
External Sector:
Remittance inflows increased by 21.6% to Rs. 839 billion, contributing significantly to the current account surplus of Rs. 161.69 billion.
Net foreign direct investment (FDI) remained positive at Rs. 5.18 billion, and the Balance of Payments recorded a surplus of Rs. 297.72 billion.
Overall Economic Indicators:
Broad money (M2) increased by 7.0%, reflecting sound monetary conditions.
The terms of trade (ToT) index increased by 9.9%, indicating favorable trade conditions.
The outstanding concessional loan extended to various sectors amounted to Rs. 154.43 billion.
Inter-Bank Transactions:
Inter-bank transactions among financial institutions reached Rs. 2872.44 billion, showcasing robust financial activities.
This comprehensive analysis provides a detailed insight into Nepal’s economic conditions, facilitating informed decision-making and policy formulation for stakeholders and policymakers alike.












Facebook Comment